Guava Optional类
Optional用于包含非空对象的不可变对象。 Optional对象,用于不存在值表示null。这个类有各种实用的方法,以方便代码来处理为可用或不可用,而不是检查null值
类声明
以下是com.google.common.base.Optional
@GwtCompatible(serializable=true)
public abstract class Optional<T>
extends Object
implements Serializable类方法

Optional示例:
import com.google.common.base.Optional;
public class GuavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]){
GuavaTester guavaTester = new GuavaTester();
Integer value1 = null;
Integer value2 = new Integer(10);
//Optional.fromNullable - allows passed parameter to be null.
Optional<Integer> a = Optional.fromNullable(value1);
//Optional.of - throws NullPointerException if passed parameter is null
Optional<Integer> b = Optional.of(value2);
System.out.println(guavaTester.sum(a,b));
}
public Integer sum(Optional<Integer> a, Optional<Integer> b){
//Optional.isPresent - checks the value is present or not
System.out.println("First parameter is present: " + a.isPresent());
System.out.println("Second parameter is present: " + b.isPresent());
//Optional.or - returns the value if present otherwise returns
//the default value passed.
Integer value1 = a.or(new Integer(0));
//Optional.get - gets the value, value should be present
Integer value2 = b.get();
return value1 + value2;
}
}看到结果
First parameter is present: false
Second parameter is present: true
10Guava Preconditions类
Preconditions提供静态方法来检查方法或构造函数,被调用是否给定适当的参数。它检查的先决条件。其方法失败抛出IllegalArgumentException
类声明
以下是com.google.common.base.Preconditions类的声明:
@GwtCompatible
public final class Preconditions
extends Object类方法

Preconditions示例:
import com.google.common.base.Preconditions;
public class GuavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]){
GuavaTester guavaTester = new GuavaTester();
try {
System.out.println(guavaTester.sqrt(-3.0));
}catch(IllegalArgumentException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {
System.out.println(guavaTester.sum(null,3));
}catch(NullPointerException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
try {
System.out.println(guavaTester.getValue(6));
}catch(IndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
public double sqrt(double input) throws IllegalArgumentException {
Preconditions.checkArgument(input > 0.0,
"Illegal Argument passed: Negative value %s.", input);
return Math.sqrt(input);
}
public int sum(Integer a, Integer b){
a = Preconditions.checkNotNull(a,
"Illegal Argument passed: First parameter is Null.");
b = Preconditions.checkNotNull(b,
"Illegal Argument passed: Second parameter is Null.");
return a+b;
}
public int getValue(int input){
int[] data = {1,2,3,4,5};
Preconditions.checkElementIndex(input,data.length,
"Illegal Argument passed: Invalid index.");
return 0;
}
}看到结果
Illegal Argument passed: Negative value -3.0.
Illegal Argument passed: First parameter is Null.
Illegal Argument passed: Invalid index. (6) must be less than size (5)Guava Ordering类
Ordering(排序)可以被看作是一个丰富的比较具有增强功能的链接,多个实用方法,多类型排序功能等
类声明
以下是com.google.common.collect.Ordering
@GwtCompatible
public abstract class Ordering<T>
extends Object
implements Comparator<T>类方法
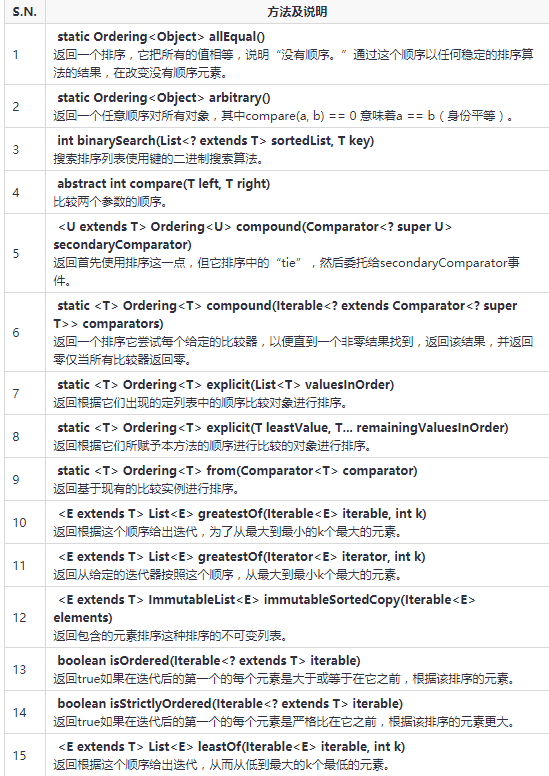

Ordering 示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import com.google.common.collect.Ordering;
public class GuavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]){
List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
numbers.add(new Integer(5));
numbers.add(new Integer(2));
numbers.add(new Integer(15));
numbers.add(new Integer(51));
numbers.add(new Integer(53));
numbers.add(new Integer(35));
numbers.add(new Integer(45));
numbers.add(new Integer(32));
numbers.add(new Integer(43));
numbers.add(new Integer(16));
Ordering ordering = Ordering.natural();
System.out.println("Input List: ");
System.out.println(numbers);
Collections.sort(numbers,ordering );
System.out.println("Sorted List: ");
System.out.println(numbers);
System.out.println("======================");
System.out.println("List is sorted: " + ordering.isOrdered(numbers));
System.out.println("Minimum: " + ordering.min(numbers));
System.out.println("Maximum: " + ordering.max(numbers));
Collections.sort(numbers,ordering.reverse());
System.out.println("Reverse: " + numbers);
numbers.add(null);
System.out.println("Null added to Sorted List: ");
System.out.println(numbers);
Collections.sort(numbers,ordering.nullsFirst());
System.out.println("Null first Sorted List: ");
System.out.println(numbers);
System.out.println("======================");
List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
names.add("Ram");
names.add("Shyam");
names.add("Mohan");
names.add("Sohan");
names.add("Ramesh");
names.add("Suresh");
names.add("Naresh");
names.add("Mahesh");
names.add(null);
names.add("Vikas");
names.add("Deepak");
System.out.println("Another List: ");
System.out.println(names);
Collections.sort(names,ordering.nullsFirst().reverse());
System.out.println("Null first then reverse sorted list: ");
System.out.println(names);
}
}看到结果
Input List:
[5, 2, 15, 51, 53, 35, 45, 32, 43, 16]
Sorted List:
[2, 5, 15, 16, 32, 35, 43, 45, 51, 53]
======================
List is sorted: true
Minimum: 2
Maximum: 53
Reverse: [53, 51, 45, 43, 35, 32, 16, 15, 5, 2]
Null added to Sorted List:
[53, 51, 45, 43, 35, 32, 16, 15, 5, 2, null]
Null first Sorted List:
[null, 2, 5, 15, 16, 32, 35, 43, 45, 51, 53]
======================
Another List:
[Ram, Shyam, Mohan, Sohan, Ramesh, Suresh, Naresh, Mahesh, null, Vikas, Deepak]
Null first then reverse sorted list:
[Vikas, Suresh, Sohan, Shyam, Ramesh, Ram, Naresh, Mohan, Mahesh, Deepak, null]Guava Objects类
Objects类提供适用于所有对象,如equals, hashCode等辅助函数
类声明
以下是com.google.common.base.Objects类的声明:
@GwtCompatible
public final class Objects
extends Object类方法
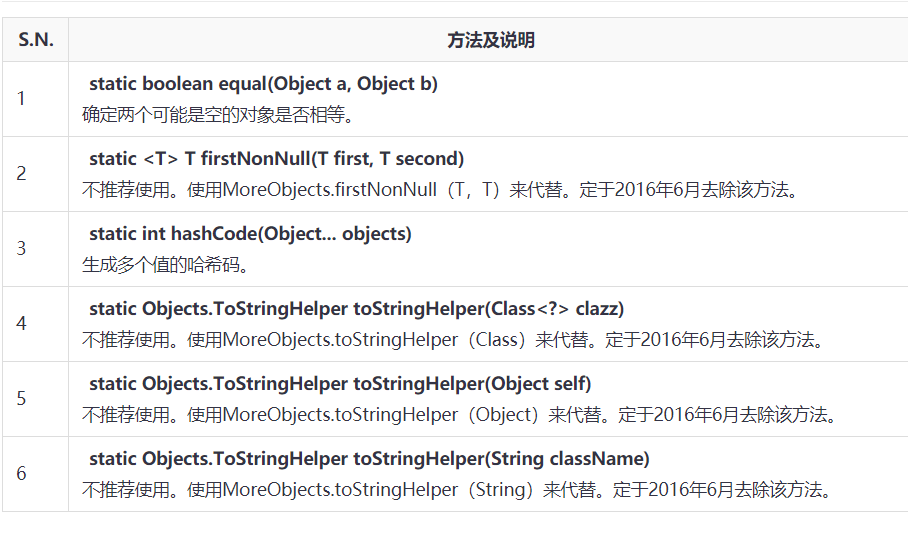
Objects 示例
import com.google.common.base.Objects;
public class GuavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]){
Student s1 = new Student("Mahesh", "Parashar", 1, "VI");
Student s2 = new Student("Suresh", null, 3, null);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.hashCode());
System.out.println(
Objects.toStringHelper(s1)
.add("Name",s1.getFirstName()+" " + s1.getLastName())
.add("Class", s1.getClassName())
.add("Roll No", s1.getRollNo())
.toString());
}
}
class Student {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private int rollNo;
private String className;
public Student(String firstName, String lastName, int rollNo, String className){
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.rollNo = rollNo;
this.className = className;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object){
if(!(object instanceof Student) || object == null){
return false;
}
Student student = (Student)object;
// no need to handle null here
// Objects.equal("test", "test") == true
// Objects.equal("test", null) == false
// Objects.equal(null, "test") == false
// Objects.equal(null, null) == true
return Objects.equal(firstName, student.firstName) // first name can be null
&& Objects.equal(lastName, student.lastName) // last name can be null
&& Objects.equal(rollNo, student.rollNo)
&& Objects.equal(className, student.className);// class name can be null
}
@Override
public int hashCode(){
//no need to compute hashCode by self
return Objects.hashCode(className,rollNo);
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getRollNo() {
return rollNo;
}
public void setRollNo(int rollNo) {
this.rollNo = rollNo;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
}看到结果
false
85871
Student{Name=Mahesh Parashar, Class=VI, Roll No=1}Guava Range类
Range 表示一个间隔或一个序列。它被用于获取一组数字/串在一个特定范围之内。
类声明
以下是com.google.common.collect.Range
@GwtCompatible
public final class Range<C extends Comparable>
extends Object
implements Predicate<C>, Serializable方法
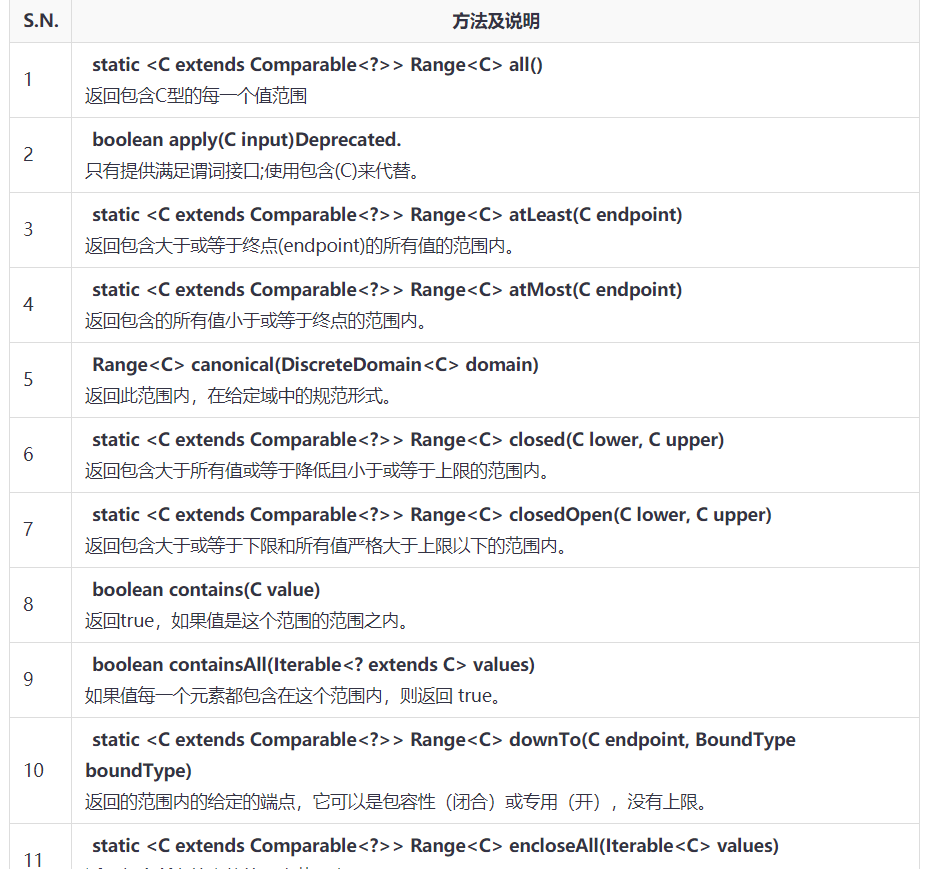
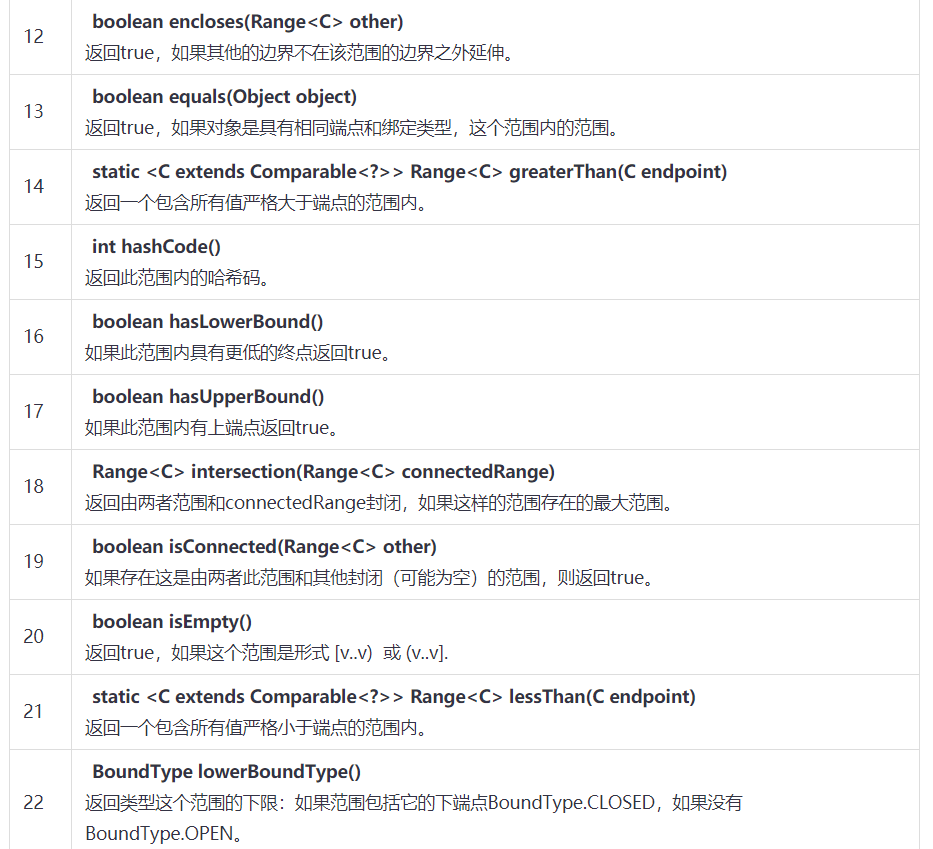
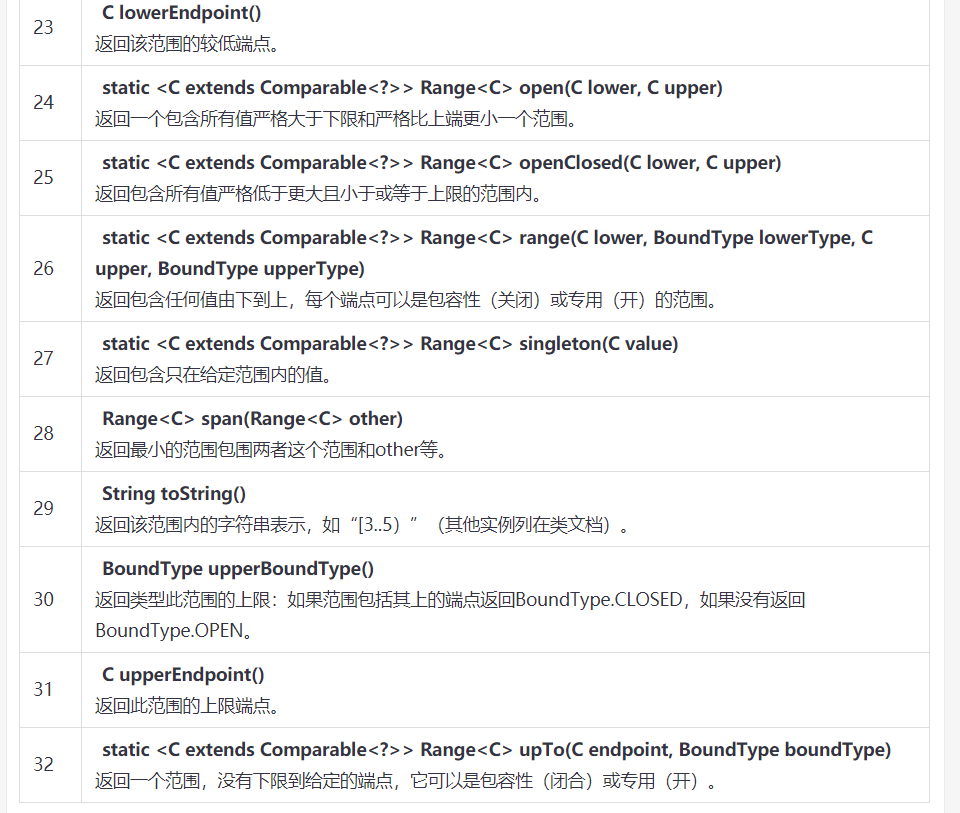
Range 例子
import com.google.common.collect.ContiguousSet;
import com.google.common.collect.DiscreteDomain;
import com.google.common.collect.Range;
import com.google.common.primitives.Ints;
public class GuavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]){
GuavaTester tester = new GuavaTester();
tester.testRange();
}
private void testRange(){
//create a range [a,b] = { x | a <= x <= b}
Range<Integer> range1 = Range.closed(0, 9);
System.out.print("[0,9] : ");
printRange(range1);
System.out.println("5 is present: " + range1.contains(5));
System.out.println("(1,2,3) is present: " + range1.containsAll(Ints.asList(1, 2, 3)));
System.out.println("Lower Bound: " + range1.lowerEndpoint());
System.out.println("Upper Bound: " + range1.upperEndpoint());
//create a range (a,b) = { x | a < x < b}
Range<Integer> range2 = Range.open(0, 9);
System.out.print("(0,9) : ");
printRange(range2);
//create a range (a,b] = { x | a < x <= b}
Range<Integer> range3 = Range.openClosed(0, 9);
System.out.print("(0,9] : ");
printRange(range3);
//create a range [a,b) = { x | a <= x < b}
Range<Integer> range4 = Range.closedOpen(0, 9);
System.out.print("[0,9) : ");
printRange(range4);
//create an open ended range (9, infinity
Range<Integer> range5 = Range.greaterThan(9);
System.out.println("(9,infinity) : ");
System.out.println("Lower Bound: " + range5.lowerEndpoint());
System.out.println("Upper Bound present: " + range5.hasUpperBound());
Range<Integer> range6 = Range.closed(3, 5);
printRange(range6);
//check a subrange [3,5] in [0,9]
System.out.println("[0,9] encloses [3,5]:" + range1.encloses(range6));
Range<Integer> range7 = Range.closed(9, 20);
printRange(range7);
//check ranges to be connected
System.out.println("[0,9] is connected [9,20]:" + range1.isConnected(range7));
Range<Integer> range8 = Range.closed(5, 15);
//intersection
printRange(range1.intersection(range8));
//span
printRange(range1.span(range8));
}
private void printRange(Range<Integer> range){
System.out.print("[ ");
for(int grade : ContiguousSet.create(range, DiscreteDomain.integers())) {
System.out.print(grade +" ");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}看到结果
[0,9] : [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ]
5 is present: true
(1,2,3) is present: true
Lower Bound: 0
Upper Bound: 9
(0,9) : [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ]
(0,9] : [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ]
[0,9) : [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ]
(9,infinity) :
Lower Bound: 9
Upper Bound present: false
[ 3 4 5 ]
[0,9] encloses [3,5]:true
[ 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ]
[0,9] is connected [9,20]:true
[ 5 6 7 8 9 ]
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 ]Guava Multiset接口
Multiset接口扩展设置有重复的元素,并提供了各种实用的方法来处理这样的元素在集合中出现
接口方法


Multiset 示例
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import com.google.common.collect.HashMultiset;
import com.google.common.collect.Multiset;
public class GuavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]){
//create a multiset collection
Multiset<String> multiset = HashMultiset.create();
multiset.add("a");
multiset.add("b");
multiset.add("c");
multiset.add("d");
multiset.add("a");
multiset.add("b");
multiset.add("c");
multiset.add("b");
multiset.add("b");
multiset.add("b");
//print the occurrence of an element
System.out.println("Occurrence of 'b' : "+multiset.count("b"));
//print the total size of the multiset
System.out.println("Total Size : "+multiset.size());
//get the distinct elements of the multiset as set
Set<String> set = multiset.elementSet();
//display the elements of the set
System.out.println("Set [");
for (String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("]");
//display all the elements of the multiset using iterator
Iterator<String> iterator = multiset.iterator();
System.out.println("MultiSet [");
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("]");
//display the distinct elements of the multiset with their occurrence count
System.out.println("MultiSet [");
for (Multiset.Entry<String> entry : multiset.entrySet())
{
System.out.println("Element: "+entry.getElement() +", Occurrence(s): " + entry.getCount());
}
System.out.println("]");
//remove extra occurrences
multiset.remove("b",2);
//print the occurrence of an element
System.out.println("Occurence of 'b' : "+multiset.count("b"));
}
}Guava Bimap接口
接口方法

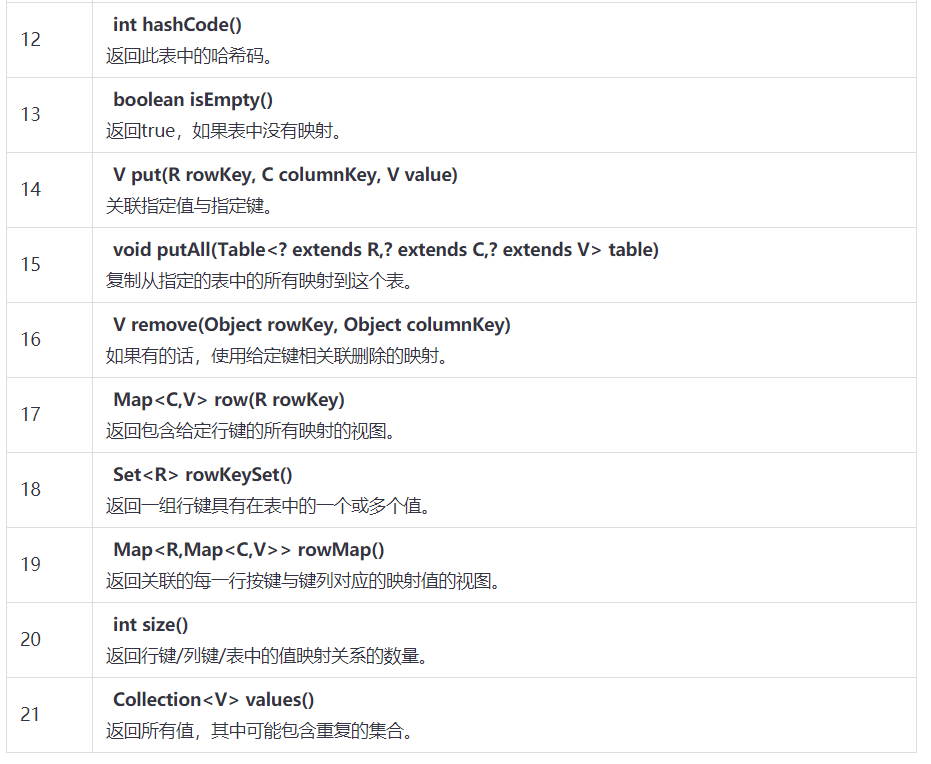
Guava Table接口
接口方法

Guava缓存工具
接口方法

Guava Joiner类
类方法


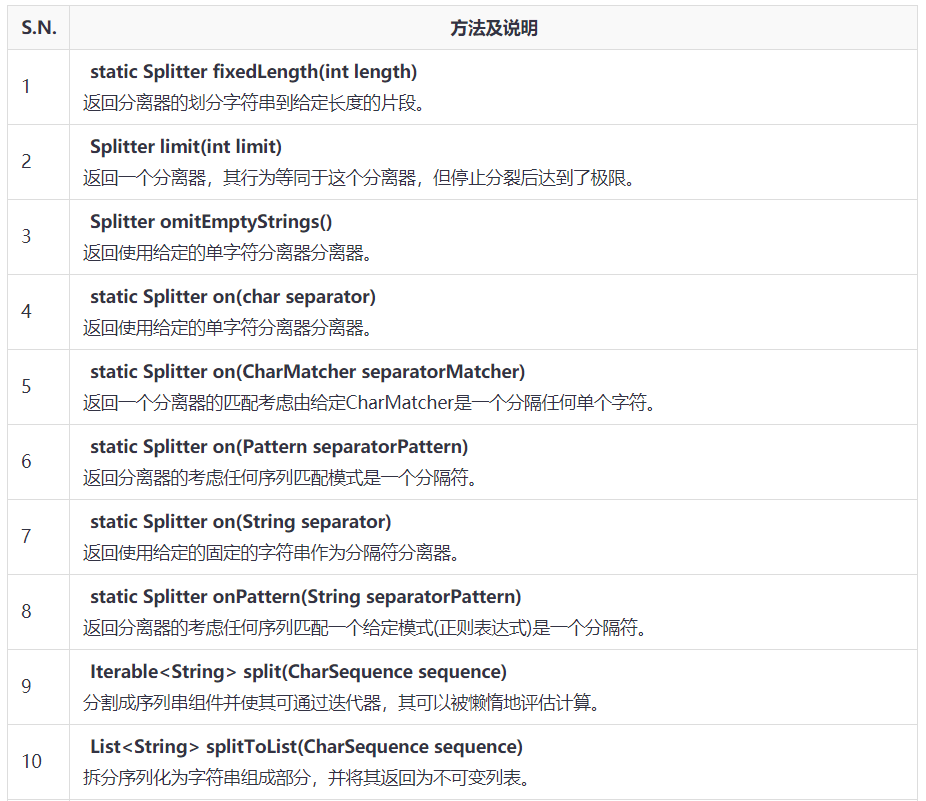
Guava Spiltter类
类方法

Guava Multimap类
接口方法


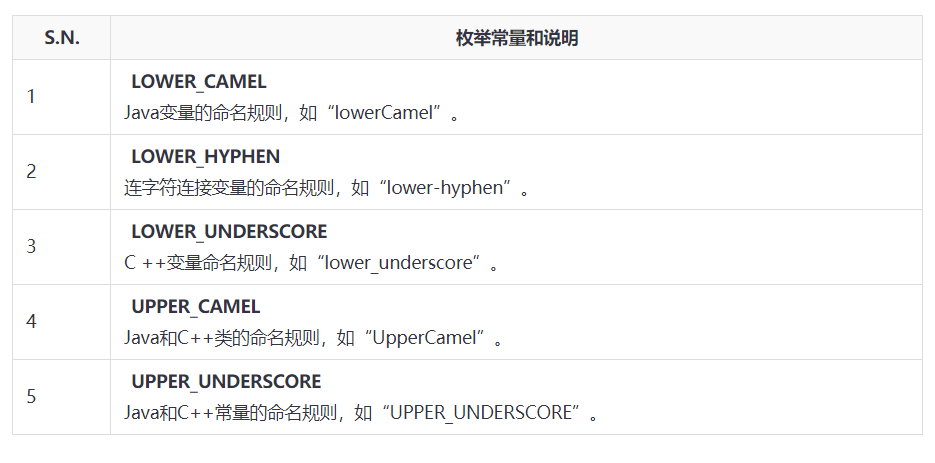
Guava CaseFormat类
CaseFormat是一种实用工具类,以提供不同的ASCII字符格式之间的转换
枚举常量
方法




